Data Types in Java
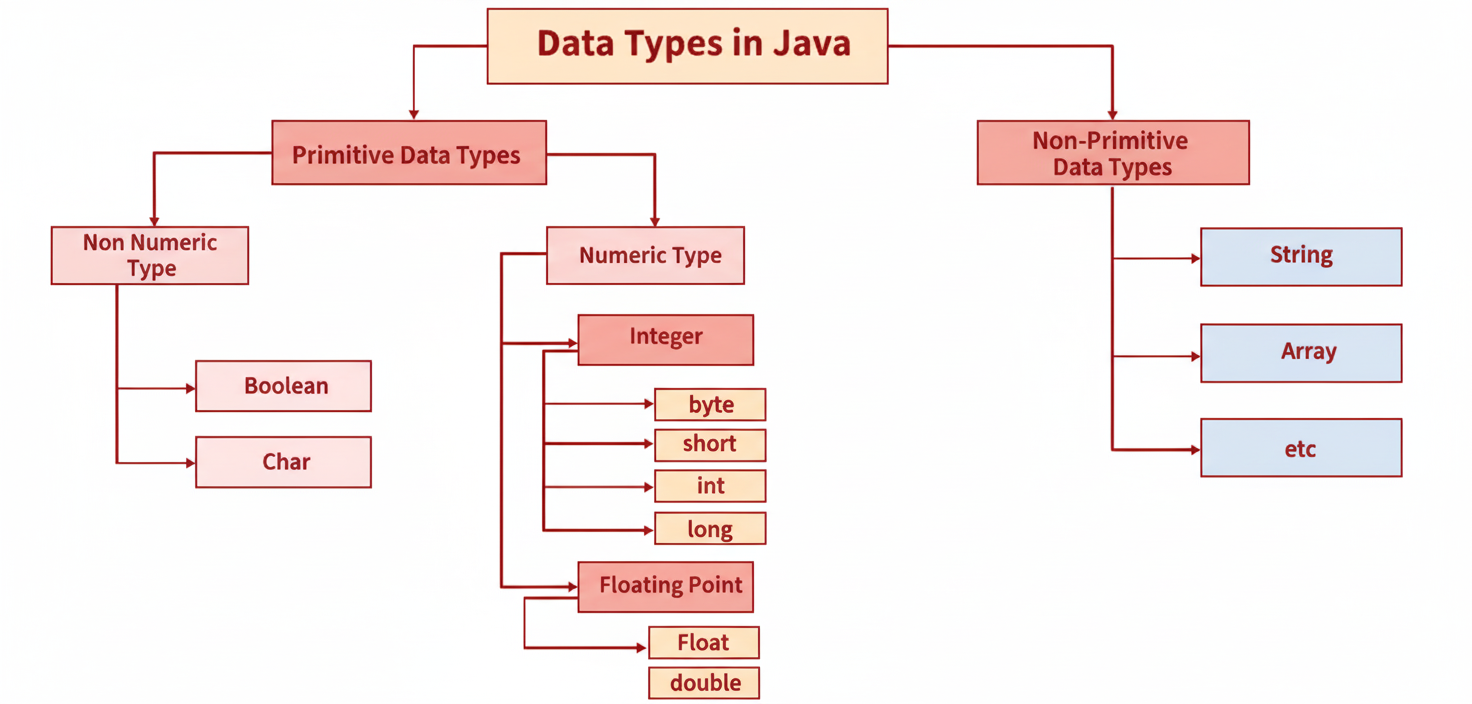
Data types in Java define the kind of data a variable can hold and the memory required to store it. They are broadly divided into two categories:
- Primitive Data Types: Store simple values directly in memory.
- Non-Primitive (Reference) Data Types: Store memory references to objects.
How Primitive Variables Are Stored
Primitive data types store the actual value directly in the stack memory.
Example:
int x = 10;- The variable x is stored in stack.
- The actual value 10 is also in the stack.
✔ Primitive = store REAL value in stack
How Non-Primitive Variables Are Stored
Non-primitive data types store only the reference (address) in stack, but the actual object is stored in heap memory.
Example:
String name = new String("John");This is what happens:
- name → stored in stack
- "John" object → stored in heap
- Stack variable name stores a reference (pointer) to the heap object.
✔ Non-primitive = stack holds reference, heap holds actual object
Primitive Data Types
Primitive types are the fundamental data types that store single values. Java defines eight primitive data types, summarized below:
| Type | Description | Default | Size | Example | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | Logical values | false | JVM-dependent (typically 1 byte) | true, false | — |
| byte | 8-bit signed integer | 0 | 1 byte | 10 | -128 to 127 |
| char | 16-bit Unicode character | \u0000 | 2 bytes | 'A', '\u0041' | 0 to 65,535 |
| short | 16-bit signed integer | 0 | 2 bytes | 2000 | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| int | 32-bit signed integer | 0 | 4 bytes | 1000, -500 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| long | 64-bit signed integer | 0L | 8 bytes | 123456789L | ±9.22e18 |
| float | 32-bit floating point | 0.0f | 4 bytes | 3.14f | ~6–7 digits precision |
| double | 64-bit floating point | 0.0d | 8 bytes | 3.14159d | ~15–16 digits precision |
