Introduction to Java
1. Definition of Java
- Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language.
- Developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle) in 1995.
- Known for its "write once, run anywhere" capability.
Java Features
• Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):
Java fully supports object-oriented programming.
• Platform Independent:
Java code can run on any system without considering OS.
• Multithreading:
Java allows running multiple tasks concurrently and can increase efficiency.
• Standard Libraries and APIs:
Java provides multiple built-in libraries and APIs for programming needs.
• Open-Source Libraries:
Java has a wide range of libraries to extend functionality and speed up development.
What is JDK (Java Development Kit) in Java
Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development environment that is developed and distributed by Oracle. It is used for building (developing) Java software applications and applets.
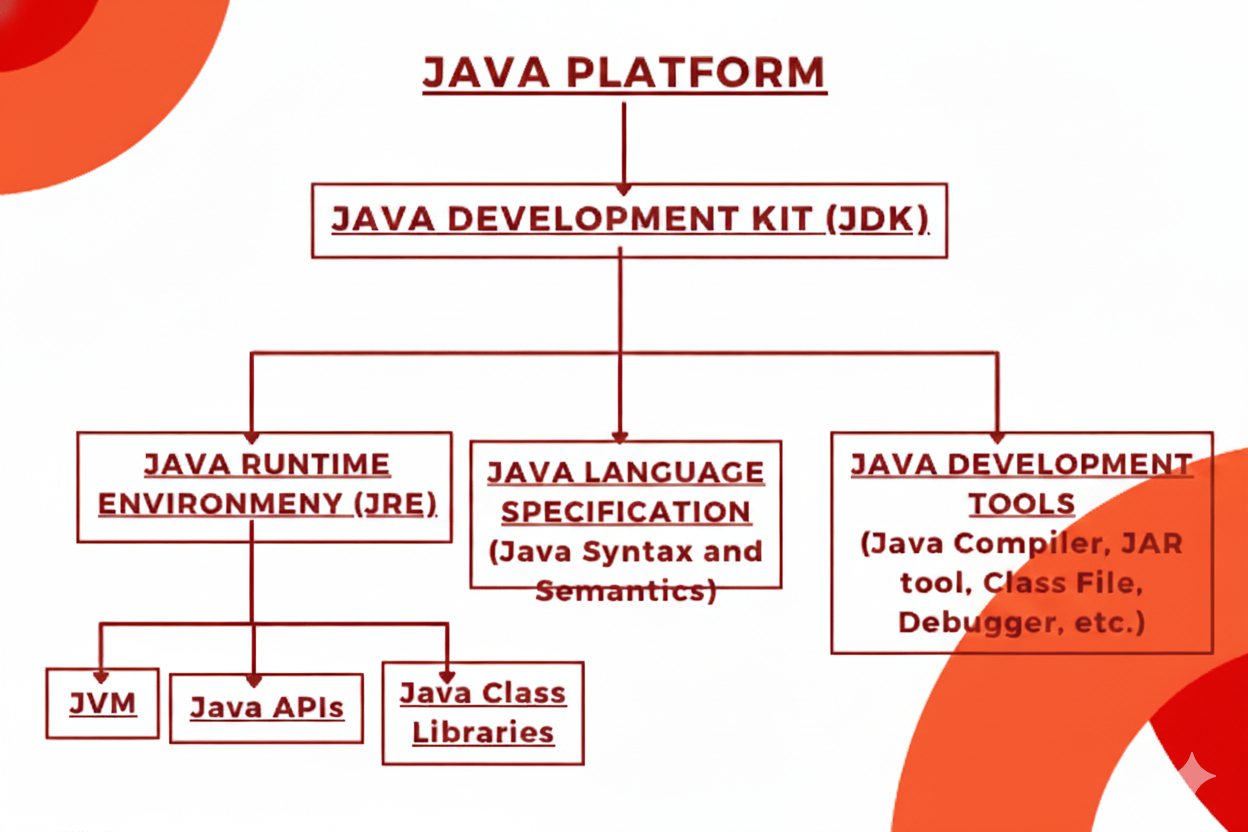
a) Java Runtime Environment (JRE):
It is an environment that is required for running (executing) a Java application. It cannot be used for the development of Java applications. It is used only for executing the application program.
Java Language Specification:
The Java language specification is a technical definition of syntax and semantics of the Java programming language.
Java Development Tools:
It consists of Java compiler, JAR tool, class file disassembler, debugger, JRE builder, etc. Java Development Tools provides everything for compiling, running, monitoring, debugging, and documenting applications.
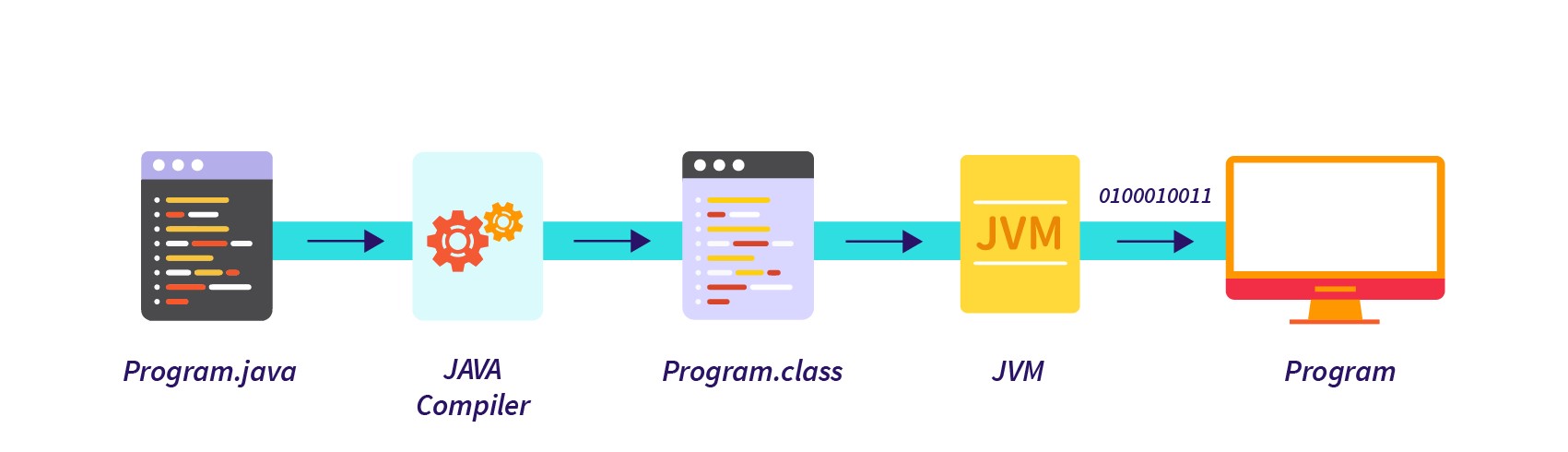
How to Run Java Programme
- Java is a high-level language.
- Java compiler called "javac" converts it to byte code (creates class file).
- JVM can read byte code and convert it to machine code then execute the programme.
- Java is platform independent because this byte code can run on any JVM. JVM takes responsibility for converting byte code to executable machine code based on OS and other dependencies.